Category: Tort Law
-
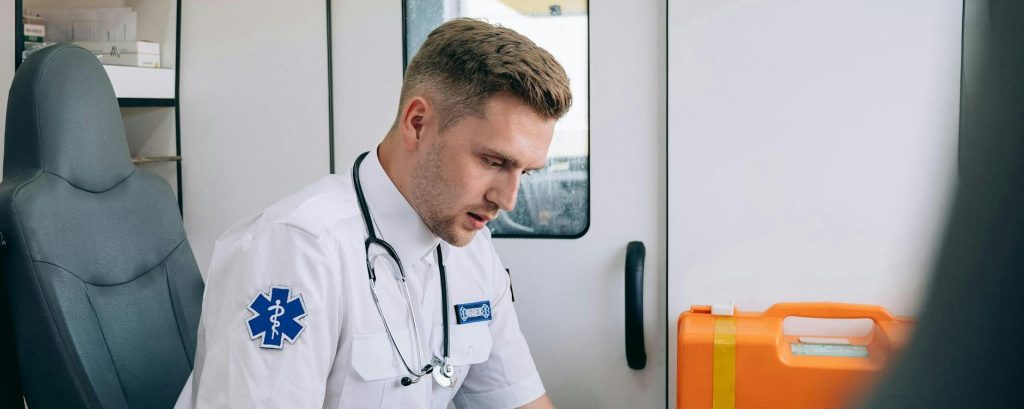

In Hegarty v Queensland Ambulance Service [2007] QCA 366, a paramedic developed psychiatric injuries after exposure to numerous traumatic events at work. The Court of Appeal allowed the State’s appeal, dismissing the employee’s actions, concluding it was difficult for supervisors to recognise his psychological distress despite training.